Community based
Wildlife and Forest
Conservation
Forests, ...
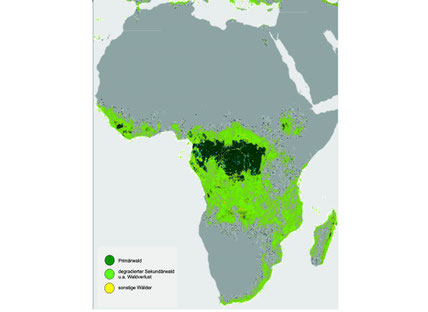
The forests of Africa cover an area of approx.
6.2 million square kilometers, more than 20 percent of the African continent.
Between 1990 and 2015, Africa lost approximately 12% of its forest area.
The African rainforest of the Congo Basin and the west coast is the second largest rainforest on earth after the Amazon with an area of approx. 2 million square
kilometers, about 5.5 times the area of Germany (area Germany 357,582 square kilometers) or almost half the size of the EU (4,381 .324 km²)
The rainforests of the Congo Basin are home to over 400 species of mammals, more than 1000 species of birds and
an
Decline of forest areas in
Africa
estimated 10,000 species of plants. Decline in forest areas in
Africa
African dry forests receive far less attention, even though they are almost 2.5 times the size of the rainforests. More than 5 times as many people as in the African rainforest depend on the dry forests as the basis of their existence.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
... Elephants ...

The number of African elephants around 1800 was estimated at 27 million
(all). A hundred years later, around 1900, it had shrunk to around 10 million (black). At the first scientific elephant count between 1973 and 1976,
there were still around 1.3 million animals (green / pink). In 2018 there were just about 400,000 (pink).
Every year, around 40,000 elephants (10%) are poached for their ivory or legally shot by trophy hunters. Elephants could have disappeared from Africa's
wilderness within a few years.
Population development of elephants in Africa
from 1800 to the present day.
Each elephant symbol represents 100,000 animals.
____________________________________________________________________________________________

... and People
The focus of our project work in Africa is on the sustainable coexistence
between people, forests and wild animals and especially the often problematic coexistence with elephants is at the forefront.
However, our work is not only limited to existing elephant areas, we are also active in regions that lie between or around elephant areas in order to explore opportunities such as
nature and species protection in rural areas.
Village communities can regain their footing and whether future
Forest degradation for daily firewood
needs
networking corridors between existing forests can be created for elephants and other
wild animals.
Our Food Forest village project in the Lumakanda region in western Kenya is located between the forests on Mount Elgon, the Mau Forest and Kenya's last inland rainforest, the
Kakamega.